
07/25 Update added below. This post was originally published on July 22nd, 2020.
Hundreds of unsecured databases exposed on the public web are the target of an automated 'meow' attack that destroys data without any explanation.
The activity started recently by hitting Elasticsearch and MongoDB instances without leaving any explanation, or even a ransom note. Attacks then expanded to other database types and to file systems open on the web.
A quick search by BleepingComputer on the IoT search engine Shodan initially found dozens of databases that have been affected by this attack. Recently, the number of wiped databases increased to over 1,800.
These attacks have pushed researchers into a race to find the exposed databases and report them responsibly before they become 'meowed.'
Cat's out of the bag
One of the first publicly known examples of a Meow attack is an Elasticsearch database belonging to a VPN provider that claimed not to keep any logs.
Discovered by researcher Bob Diachenko, the database was initially secured in July only to become exposed again five days later.
The second time, though, the owner no longer received a well-intended notification. Instead, they got ‘meowed,’ with almost all records getting wiped.
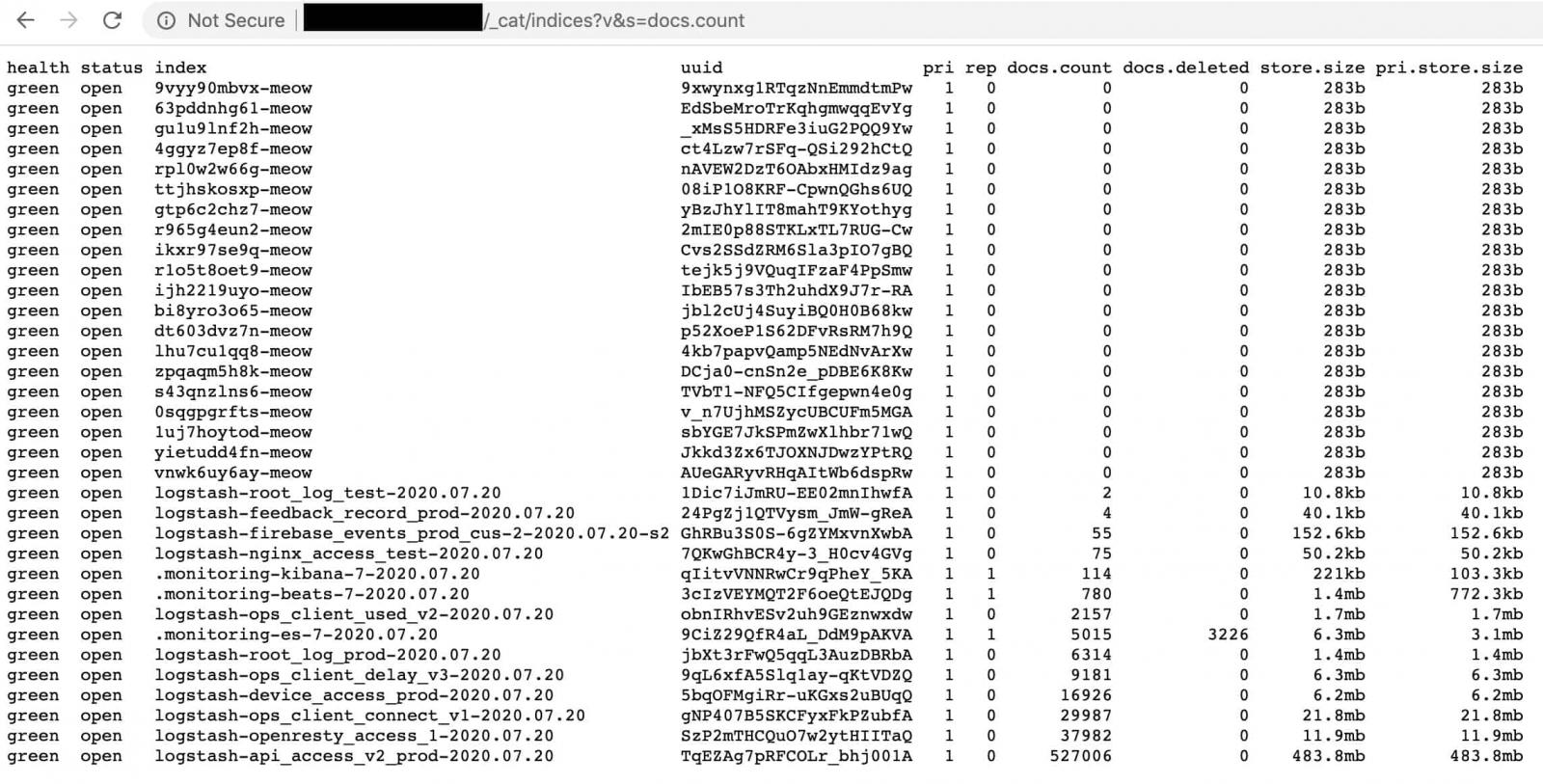
Diachenko told BleepingComputer that there are not many details about the attacker or the purpose of their actions. He says that the attack appears to be an automated script that “overwrites or destroys the data completely.”
Researchers first observed the ‘meow’ database attacks at the beginning of the week. They could be the work of a vigilante trying to give administrators a hard lesson in security by raining destruction on unsecured data.
Victor Gevers, the chairman of the non-profit GDI Foundation, saw this type of attack, too. He says that the actor is also attacking exposed MongoDB databases, hitting as much as they can.
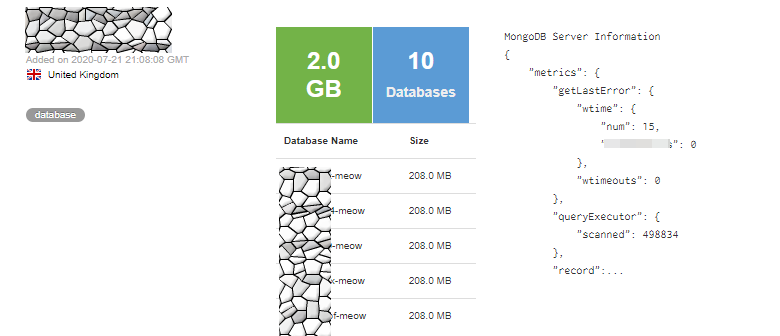
He also saw the first ‘meow’ attacks a few days ago, with a recent one occurring on July 22, just a couple of hours after a GDI volunteer disclosed it responsibly to the owner.
The researcher observed on Thursday that whoever is behind the 'meow' attack is apparently targeting any database that is insecure and reachable over the internet.
He saw these data-wiping attacks on systems running Cassandra, CouchDB, Redis, Hadoop, Jenkins, as well as against network-attached storage devices.
At the time of writing, BleepingComputer saw that 'meow' attacks impacted mostly Elasticsearch databases (1,395), followed by MongoDB (383), and Redis (54). This amounts to 1,832 but the real figure is higher as search engines start indexing the other database types. We will update the numbers when we get result for other database types.
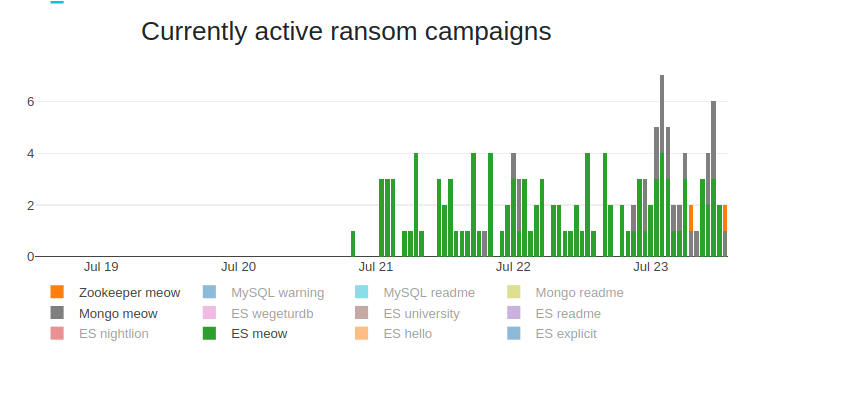
According to LeakIX, a project that indexes open services, Apache ZooKeeper has been added on the list of "meow" attacks.
07/25 Update: The Meow attacks continue to escalate with almost 4,000 databases deleted as of Saturday, July 25th.
A new search on Saturday using Shodan shows that more than 3,800 databases have entry names matching the 'meow' attack. More than 97% of them are Elastic and MongoDB.
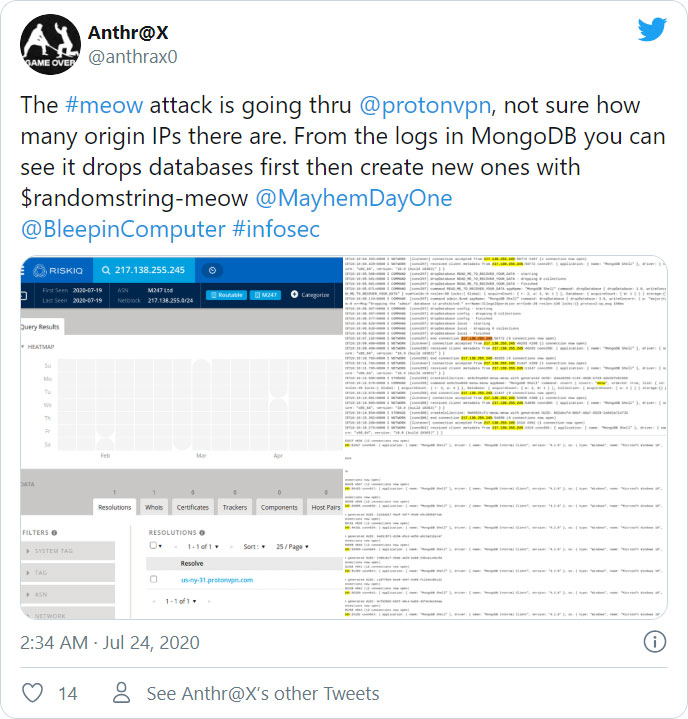
While it is still not known why the threat actors are wiping databases, a security researcher named Anthr@X discovered that the attacks are being conducted via ProtonVPN IP addresses.
Obstructing researchers
If behind these incidents are positive intentions, sometimes nothing good comes out of them and valuable data that could be lost in the process.
Data leaks from unsecured MongoDB and Elasticsearch instances reachable over the public internet are on a descending curve, but there is still some “very sensitive” information exposed.
As Gevers puts it, “some leaks bring bad things to the light, which need to be shared,” and wiping them brings benefits to no one.
“It is becoming a race to find these leaks as early as possible. This reduces the amount of time that can be spent on researching and reporting” - Victor Gevers
Whoever is behind the 'meow' attacks is likely to keep on targeting unsecured databases, aggressively destroying them. Administrators should make sure that they expose only what needs to be exposed and make sure the assets are properly secured.
Update [July 25, 2020]: Added image with overall status of 'meow' attacks from LeakIX. Recalculated amount of deleted databases due to Meow attacks.


Comments
the_moss_666 - 3 years ago
"“some leaks bring bad things to the light, which need to be shared,” and wiping them brings benefits to no one."
I disagree. Erasing data that shouldn't exist in the first place benefits everyone in those databases. Researcher searching through this data would be more severe breach than the first one. I don't totally agree with it (but erased database is a little bit better than leaked database), but I don't think "benefits no one" is a true statement.
It's also possible it's an attempt to destroy evidence of stealing the data.
Some-Other-Guy - 3 years ago
"destroys data without any explanation"
Really?
You need an explanation?
You should not leave data unsecured!
Especially "OUR" data
Data you aquired by deception, blackmail, extortion, backdoors and confusing legalese for your own personal profit at "OUR" espense
Wiping this data was just as Legal as you having the data and/or leaving it unsecured !
Keep up the good work!
Kudos!
Meow Meow Meow Meow
You've had enough time to delete "our" data and/or secure all other data that you "think" you own
Times UP!
I completely agree with whoever did this!
It was the right thing to do!
How's that?
As good an explanation as any....
Makes sense to me!
Meow
costiusha - 3 years ago
It is not clear from the article how meow manages to connect to elasticsearch. Aren't these public facing servers protected with firewalls? Aren't specific ports blocked? How can one protect against meow? The article doesn't talk about defense and about what's wrong with the hacked servers.